The Impact of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) is gaining prominence in a wide range of areas. Everything from autonomous cars, video games, healthcare products, and space programs has benefited significantly from AR capabilities.
Coined in the 1990s by Boeing researcher Thomas P Caudell, the term “augmented reality” refers to the software systems that overlay digital information onto physical objects. Augmented reality allows for the integration of virtual objects i.e images, texts, and effects to enhance the real-world experience of users.
Unlike virtual reality, which occurs in virtual environments, augmented reality interacts with the physical world and superimposes virtual, visual information on top it, allowing us to experience our environments in a more dynamic and engaging way.
In healthcare, AR is paving a new way for medical professionals to learn, deliver personalized care and save lives. The potential of AR is immense and far-reaching. Here are some key areas in healthcare that AR is already making a huge difference.
Telemedicine
While telemedicine has been around for decades, it has gained renewed attention in recent months due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The pandemic shed light on the challenges facing healthcare workers, especially the issue of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) shortages, and disparate systems that have left many healthcare workers on the frontline exposed to coronavirus.
According to Reuters, more than 90,000 healthcare workers worldwide have been infected with COVID-19. That estimate is based on data collected on 30 countries. If the infection rate of healthcare workers, about 6 percent, is taken into account, the number of infected healthcare workers globally could rise to 200,000 according to the International Council of Nurses (ICN) chief executive officer, Howard Catton.
This development has prompted hospitals and other healthcare providers across the globe to turn to communication and collaboration technologies such as augmented reality to help combat the challenges posed by COVID-19.
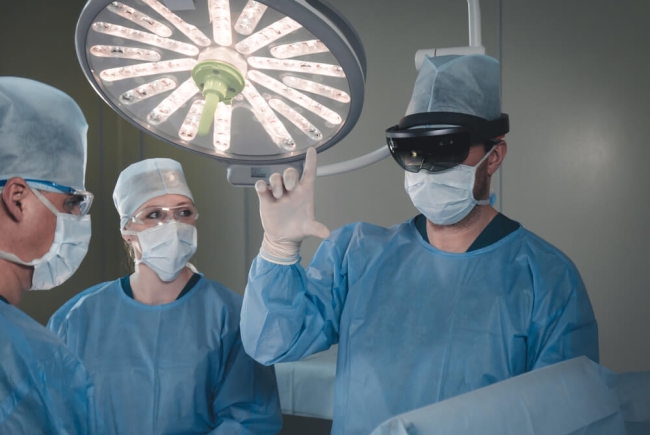
Saint Mary's Hospital in London is one of the first to deploy augmented reality technologies to reduce the number of staff exposed to patients with coronavirus. The hospital is testing Microsoft's HoloLens in collaboration with other hospitals in London to transmit vital data, images, and audio from a patient examination to doctors and nurses in remote locations via Microsoft's video conferencing app. This minimizes the risk of exposure, reduces the amount PPE needed, and helps patients get the care they need from any location.
Surgery
In its 2015 report, the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery estimated that about 5 billion people around the world lack access to safe and affordable surgery. While medical technologies have advanced tremendously over the past decade, there's still a lot of room for improvement.
Prior to surgery, surgeons usually study grayscale images, sometimes hundreds of them, to create visual estimation of patient anatomy. However, committing these images to memory and recalling them in operating theater can be difficult. This led Medivis, a medical device company founded by a team of doctors and engineers to explore solutions that allow doctors to see what’s going on inside a patient’s body in real-time, and better visualize and plan for surgical procedures.
At the Cleveland Clinic, an academic medical center based in Ohio, a team of 11 surgeons in 2017 successfully carried out a facial transplant on a woman named Katie Stubblefield (the youngest ever recipient of facial transplant in the U.S.) with the aid of AR technology.
Dr. Brian Gastman who led the team describes AR's role in the procedures "what we were able to do is superimpose images onto her (Katie) using…a HoloLens. This is a device you can wear on your head. And it allows the surgeon and the physician, the caregivers to still see the environment around them, including Katie. But what we're able to do is project different images onto Katie, different scenarios, say, of the different type of cranial structures, maybe how much they wanted to take or what they didn't want to take. So it allowed the physicians to look at different scenarios on the fly."
Medical Training
Institutions are embracing cutting-edge technologies such as AR in a bid to transform medical education and training. At the Royal College of Surgeons in London, doctors are exploring AR-based 3D holograms and other software tools to replace cadaver-based training.
Traditional cadaver-based training barely provided students in the theater to attain hands-on training with surgical procedures, making learning difficult and disengaging. With AR technologies, students can learn at their own pace, repeat procedure until it sinks in, and gain real-time access to the latest surgical technique. This not only helps students learn in more engaging ways but also helps reduce costs and democratizes access to training.
Equipment Training, Demos and Sales Coaching
COVID-19, social distancing, and deferral of medical conferences are redefining how physicians are trained on new equipment and how companies demo medical devices.
Even before the pandemic, physicians were often presented with new hardware and software upgrades for the equipment they are using. In critical industries such as healthcare, it’s essential to stay up to date with the latest developments and best practices.
In a recent podcast interview, Christopher Lind, head of Global Digital Learning at GE Healthcare reveals how his company is finding success with AR technology provided by CGS’s Teamwork AR. The use of AR in equipment training is helping medical device manufacturers like GE train sales teams in remote settings and demo products and key upgrades to healthcare professionals.
The falling cost of augmented reality (AR) hardware and the growing possibilities it proposes to healthcare means that we can expect to see many more use cases for this immersive technology. There is a budding interest in using VR/AR for neuropsychological conditions, clinical research, medical practices, patient education, and therapeutic delivery, as well as pharmacy and drug design. To learn more about how augmented reality can enhance your ongoing initiatives, watch our Director of R&D discuss use cases for GE Healthcare .
Resources
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6636465/
https://www.blippar.com/blog/2018/06/08/history-augmented-reality
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/lu/Documents/life-science...
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-nurses/over-90000-...
https://www.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/lancet/PIIS0140-6736(15)60160-X.pdf
https://www.medivis.com/surgicalar
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/magazine/2018/09/face-transplant-kati...
https://www.washingtonpost.com/washington-post-live/2019/06/13/transcrip...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7082471/
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/life-science...
https://www.cgsinc.com/blog/7-takeaways-our-digital-upskilling-webinar-h...