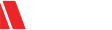Topics
IT Downtime: How to Calculate the Costs and Control the Risks

Reliability. Scalability. Availability.
These business buzzwords may seem ubiquitous, but they represent legitimate concerns for IT organizations everywhere. In an environment that is driven by global commerce and fast-paced technology innovation, providing a dependable IT infrastructure has become necessary to stay ahead of the competition. Inadequacy in this area could lead to enormous costs, negative brand impact and damaging downtime.

This article will address the direct and indirect implications of IT downtime as well as the systems, applications and data solutions that are being implemented through Remote Monitoring and Management to mitigate risks and optimize profitability.
Coping with the inevitability of downtime
The scope of the risk stretches beyond the actual cost of interruption. A company’s reputation and bottom line become vulnerable when outages have harmful impacts on the customer experience. Some businesses spend up to 200 minutes per outage to resolve these issues.1 The direct implications of downtime and the more hidden ripple effects on the business make it critical for IT organizations to find a better way to handle this problem.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, downtime is unacceptable. Yet, with IT teams focused on trying to support various devices in multiple locations; handling large system breaks and repairs, downtime is almost inevitable. And while IT has become one of the most important and fastest-growing departments of any business in recent years, the more resources and time being spent on resolving downtime complications means less resources and time being spent on an IT team’s core strengths—mobility, analytics, improved omnichannel customer interactions.
Costs: Tangible and Intangible
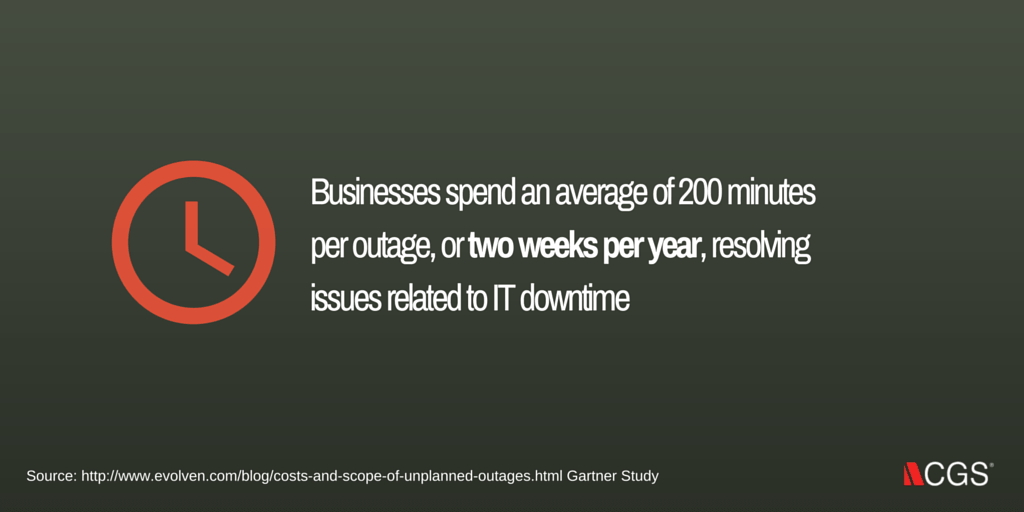
For a company, planned and unplanned outages can bring upon a flurry of costs and repercussions that are both tangible and intangible; some of which you may not have considered. The charts, formulas and figures provided in this paper will allow you to personalize the calculations to your organization and help you quantify the real costs of downtime.
These costs can be attributed to a number of factors with perhaps the three biggest being (1) business disruption, (2) impact on loyalty and reputation and (3) lost revenue.
Business Disruption in Productivity
A recent Gartner study shows that the average computer network outage can cost a company nearly $72,000 per hour2. This number is staggering, considering that it is almost as much as the average IT professional’s yearly salary.4 Business disruption affects the IT team’s day-to-day priorities including SLAs with other areas and departments of the business such as marketing, sales, customer service, financial operations, HR, legal, etc.
Impact on Loyalty and Reputation
Disruptions can put a company’s reputation at stake. One lag or interruption could mean a disturbance in the consumer experience or even lost business. Because today’s customers expect to access information and services easier and faster than ever, it is critical for businesses to not only keep up with customer expectations at all times, but exceed them. According to Bain & Company, a customer is four times more likely to defect to a competitor for service-related problems than issues related to price.
To more accurately assess total lost sales, the impact must reflect the lifetime value of customers who permanently defect to a competitor. If a large percentage of customers typically increase loyalty after a satisfactory buying experience, the opposite will be true if the experience was not positive.5
Lost Revenue
Lost revenue is a reality that no company wants to accept. The easiest way to estimate the probable loss of revenue from downtime on an annual basis is with this simple equation:
 Lost Revenue = (GR/TH) x I x H
Lost Revenue = (GR/TH) x I x H
GR: gross yearly revenue, TH: total yearly business hours I: percentage impact, H: number of hours of downtime
The final calculation is based on two factors: 1) The organization’s capacity to recuperate lost business during the outage; and 2) The lifetime significance of consumers who have permanently sought goods or services with the competition. In some industries, such as retail or hospitality where there is seasonality and peak periods, downtime can translate into millions of dollars of profit loss.
Industry Implications
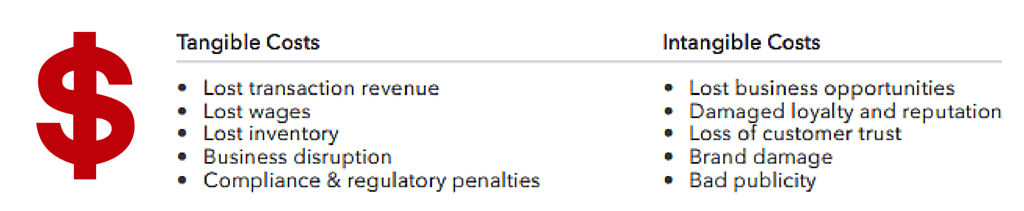
Every minute of downtime can mean thousands or even millions of dollars in costs and/or lost revenue. Across all industries, IT downtime costs about $26.5 billion in lost revenue each year.6 The average downtime costs per industry vary:7
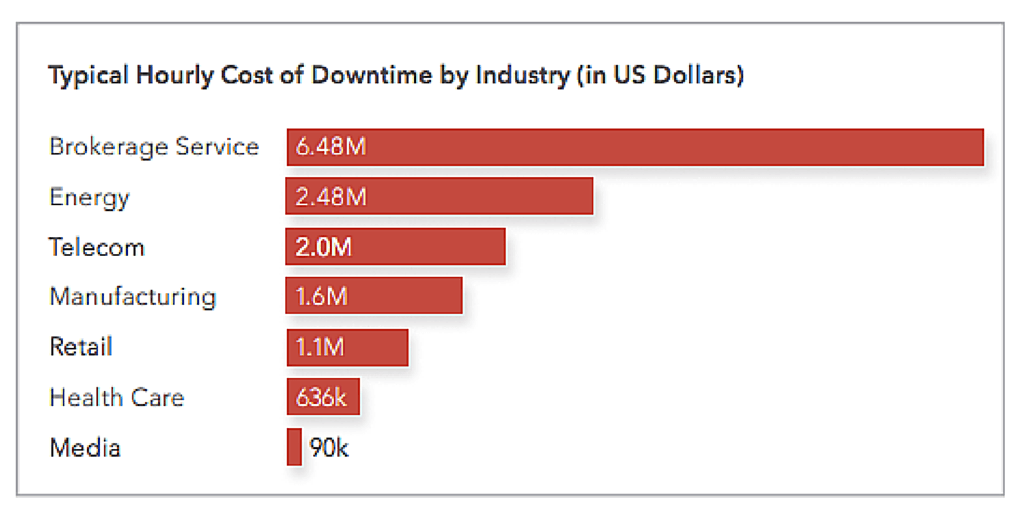
Company Implications
An organization’s infrastructure is the foundation to compete effectively. Regardless of the industry, it is imperative to take a more predictive approach to measuring, tracking and analyzing the impact of downtime. Appropriate monitoring and hourly calculation will assist in helping your company decide how much to invest in infrastructure solutions and services.
Productivity: Number of employees affected, duration of outage, average labor rate and percentage of productivity loss
Revenue: Customers, suppliers, financial markets and business partners8
Damaged Reputation & Loyalty: Direct loss, compensatory payments, lost future revenue and billing & investment loss
Even in the face of multiple influencers, the average company cannot afford even one outage. Some 93% of businesses that have lost availability in their data center for 10 days or more have filed for bankruptcy within one year.8 While zero downtime is impossible, according to the “Information Technology and Intelligence Corporation High Availability” survey, 60% of companies require over 99% availability.9
The ultimate goal is to identify the sources of downtime and calculate their costs to gain the necessary business insights needed to reduce them. After viewing all quantifiable and brand-related costs, your company should be able to determine the effect downtime has on both your financial value as well as your market advantage. For many businesses, outsourcing this role may make the most sense, allowing them to embrace a model where IT staff energies are refocused on core competency rather than management.
Important Factors of RMM
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) has become a strategic initiative for companies looking to address their downtime concerns. As Michael Brandi, Vice President CGS Technology Outsourcing, states: “RMM can create a competitive advantage by reducing the downtime an organization faces compared to its competitors, and freeing technical resources time to pursue revenue-generating projects instead of performing maintenance.”
Some of the most notable RMM functions include:
• Gathering information about client software and hardware, identifying licensing position and hardware end of life
• Proactive monitoring to anticipate issues and address them before they impact operations
• Providing patch management and anti-virus to ensure your systems are protected
• Offering issue resolution and alerting
• Backup monitoring configuration and testing
• Reporting and analytics to identify and address trends
RMM allows organizations to easily and seamlessly manage their technology infrastructure by providing remote support to all technological areas; ranging from mobile devices to entire company networks.
Simply stated, RMM decreases a firm’s chances of downtime due to 24x7x365 management of your IT environment and also provides proactive notifications to drive instant awareness of issues, resolutions and outcomes.
RMM: The Key to Proactively Eliminating Downtime
In a recent Hurwitz & Associates survey, IT leaders were asked how they view and integrate Remote Monitoring and Management into their operations. More than 70 percent of the respondents saw RMM services as a way to free up internal IT staff to focus on core business initiatives rather than break/fix activities that consume so much of their time.
While IT professionals continue to deliver the essential network support that their company needs, an outsourcing RMM partner can provide uninterrupted expert focus on the major network malfunctions that affect consumers and overwhelm nearly 80% of an IT department’s time and more than 57% of their budget.
A key success factor in planning for the pace of change is decided by the business and not the outsourcer. RMM is an important first step in transitioning from a purely on premise model to proactively managing and optimizing your environment with the power of world-class certified engineers across a diverse set of infrastructure technologies supporting your operation. Organizations will now have the agility facilitated by RMM to incorporate other optimization initiatives, such as managed cloud.
- Frank Bianchi, Vice President CGS Technology Outsourcing
With the pace of technological change accelerating, organizations are increasingly adopting a new business model that allows IT staff to keep up with the tools, knowledge and certifications necessary to manage core business initiatives. Leading IT organizations are seeking out companies that specialize in RMM and have the necessary resources, expertise and ability to make the required investments to serve as a partner and extension of the organization. These firms are finding that the benefits reach beyond mitigating risk and also facilitate other steps toward modernization.
REFERENCES
1 http://www.evolven.com/blog/costs-and-scope-of-unplanned-outages.html Gartner Study
2 http://www.evolven.com/blog/costs-and-scope-of-unplanned-outages.html IT Process Institute
3 http://www.evolven.com/blog/costs-and-scope-of-unplanned-outages.html
4 Glassdoor.com
5 http://www.businesscomputingworld.co.uk/assessing-the-financial-impact-o...
6 http://www.evolven.com/blog/costs-and-scope-of-unplanned-outages.html
7 http://www.strategiccompanies.com/pdfs/Assessing%20the%20Financial%20Imp...
8 Schneider Electric data center
9 http://searchcio.techtarget.com/podcast/Trends-in-high-availability-and-...
10 http://www.zdnet.com/article/heres-what-your-tech-budget-is-being-spent-on/